FABRIC: A planar textile structure produces by interlacing yarns, fibers, or filaments.
FABRIC CONSTRUCTION: The details of structure of fabric. Includes such information as style, width, type of knit of weave, threads per inch in warp and fill, and weight of goods.

FABRIC CRIMP: The angulation induced between a yarn and woven fabric via the weaving or braiding process.
FABRIC CRIMP ANGLE: The maximum acute angle of a single weaving yarn’s direction measured from a plane parallel to the surface of the fabric.
FABRIC SETT: The number of warp threads per inch, or other convenient unit.
FABRIC STABILIZER: Resin or latex treatment for scrims used in coated fabric manufacture to stabilize the scrim for further processing.
FACE: The correct or better-looking side of a fabric.
FACING: A lining or trim that protects the edges of a garment especially at collars, cuffs, and front closings.
FACONNÉ: A broad term for fabrics with a fancy-type weave made on a Jacquard or dobby loom.
FADE-OMETER®: Laboratory device used to determine the fastness of a colored fabric to exposure to light. The test pieces are rotated around a light source simulating the sun’s rays at 45° N latitude in July between the hours of 9 a.m. and 3 p.m. Fabrics are rated by visual comparison with a gray scale according to degree of fading.
FAILLE: A soft, slightly glossy woven fabric made of silk, rayon, cotton, wool, or manufactured fibers or combinations of these fibers and having a light, flat crossgrain rib or cord made by using heavier yarns in the filling than in the warp.
FALSE-TWISTING: See TEXTURING, False-Twist Method. FANCY YARN: See NOVELTY YARN.
FASCIATED YARN: Yarns consisting of a core of discontinuous fibers with little or no twist and surface fibers wrapped around the core bundle.
FASHIONING: The process of shaping a fabric during knitting by increasing or decreasing the number of needles in action. Fashioning is used in manufacturing hosiery, underwear, and sweaters.
FASTNESS: See COLORFASTNESS.
FATIGUE: Refers to the resistance of a material to weakening or failure during alternate tension-compression cycles, i.e., in stretch yarns, the loss of ability to recover after having been stretched.
FEEL: See HAND.
FELL: 1. The end of a piece of fabric that is woven last. 2. In weaving, the last filling pick laid in the fabric at any time.
FELT: 1. A nonwoven sheet of matted material of wool, hair, or fur, sometimes in combination with certain manufactured fibers, made by a combination of mechanical and chemical action, pressure, moisture, and heat. 2. A woven fabric generally made from wool, but occasionally from cotton or certain manufactured fibers, that is heavily shrunk and fulled, making it almost impossible to distinguish the weave.
FELTING: 1. The process of exposing wool fibers alone or in combination with other fibers to mechanical and chemical action, pressure, moisture, and heat so that they tangle, shrink, and mat to form a compact material. Felting is generally carried out in a fulling mill. (Also see FULLING.) 2. See NEEDLEPUNCHING and NEEDLED FABRIC.
FESTOON DRYER: A dryer in which cloth is suspended in loops over a series of supporting horizontal poles and carried through the heated chamber in this configuration.
FIBER: A unit of matter, either natural or manufactured, that forms the basic element of fabrics and other textile structures. A fiber is characterized by having a length at least 100 times its diameter or width. The term refers to units that can be spun into a yarn or made into a fabric by various methods including weaving, knitting, braiding, felting, and twisting. The essential requirements for fibers to be spun into yarn include a length of at least 5 millimeters, flexibility, cohesiveness, and sufficient strength. Other important properties include elasticity, fineness, uniformity, durability, and luster. (Also see MANUFACTURED FIBER and NATURAL FIBER.)
FIBER ARCHITECTURE: The spatial arrangement of fibers in the preform. Each architecture has a definite repeating unit.
FIBER DISTRIBUTION: In a web, the orientation (random or parallel) of fibers and the uniformity of their arrangement.
FIBERFILL: Manufactured fibers that have been specially engineered for use as filling material for pillows, mattress pads, comforters, sleeping bags, quilted outerwear, etc. Polyester fibers are widely used.

FIBER MIGRATION: See MIGRATION, 2.
FIBER NUMBER: The linear density of a fiber expressed in units such as denier or tex. (Also see FINENESS.)
FIBER PLACEMENT: In general, refers to how the piles are laid into their orientation, i.e., by hand, by a textile process, by a tape layer, or by a filament winder. Tolerances and angles are specified. Microprocessor-controlled placement that gives precise control of each axis of motion permits more intricate winding patterns than are possible with conventional winding and is used to make composites that are more complex that usual filament-wound structures.
FIBER-REACTIVE DYES: See DYES.
FIBRETS: Very short (<1mm), fine (diameter <50g) fibrillated fibers that are highly branched and irregular resulting in very high surface area. Fibrets can be produced from a number of substances including acetate, polyester, nylon, and polyolefins. By selection of polymer type and incorporation of additives, they can be engineered to meet a range of specialized requirements.
FIBRIDS: Short, irregular fibrous products, made by mixing a dilute polymer solution with a nonsolvent with agitation. They can also be made by flash spinning and breaking up the resulting filaments. Used in felts, in papermaking, for filtration product, etc. (Also see FIBRETS.)
FIBRIL: A tiny threadlike element of a synthetic or natural fiber.
FIBRILLATED-FILM YARN: See SLIT-FILM YARN.
FIBRILLATION: The act or process of forming fibrils. The act of breaking up a fiber, plastic sheet, or similar material into the minute fibrous elements from which the main structure is formed.
FILAMENT: A fiber of an indefinite or extreme length such as found naturally in silk. Manufactured fibers are extruded into filaments that are converted into filament yarn, staple, or tow.
FILAMENT COUNT: The number of individual filaments that make up a thread or yarn.
FILAMENT NUMBER: The linear density of a filament expressed in units such as denier or tex. (Also see FINENESS.)
FILAMENT WINDING: In the fabrication of composites, the process of placing reinforcing fibers over a rotating form, (mandrel) to make the product shape. Prepreg fibers or dry fibers that are treated in a resin bath immediately prior to winding may be used. The wound form can be cured or consolidated after the fiber winding is complete to product specifications.
FILAMENT YARN: A yarn composed of continuous filaments assembled with or without twist. (Also see YARN.)
FILLER: A nonfibrous material added to a fabric to increase its weight or to modify its appearance or hand. Also referred to as back-sizing. Examples of fillers are insoluble clays or gypsum, starches, and gums.
FILLET: A long, narrow strip of wire card clothing with which the doffer and cylinder of the card are spirally wrapped.
FILLING: In a woven fabric, the yarn running from selvage to selvage at right angles to the warp. Each crosswise length is called a pick. In the weaving process, the filling yarn is carried by the shuttle or other type of yarn carrier.
FILLING BAND: See MIXED END or FILLING. FILLING BARRÉ: See BARRÉ.
FILLING BOW: See BOW.
FILLING SKEWNESS: See SKEWNESS. FILLING SNARL: See SNARL.
FILM YARN: See SLIT-FILM YARN.
FILTER AID: A powder added to a solution to be filtered that forms a porous bed to improve filtration.
FILTER CLOTH: Any cloth used for filtering purposed. Nylon, polyester, vinyon, PBI, and glass fibers are often used in such fabrics because they are not affected by most chemicals.
FILTER FABRICS: See GEOTEXTILES and FILTER CLOTH.
FINDINGS: 1. Miscellaneous items attached to garments and shoes during manufacture. Included are buttons, hooks, snaps, and ornaments. 2. Miscellaneous fabrics in garments such a zipper tapes, linings, pockets, waistbands, and facings.
FINE END: 1. A warp yarn of smaller diameter than that normally used in the fabric. 2. A term for a defect in silk warp yarn consisting of thin places that occur when all the filaments required to make up the full ply are not present. This condition is generally caused by poor reeling.
FINENESS: 1. A relative measure of fiber size expressed in denier or tex for manufactured fibers. For cotton, fineness is expressed as the mean fiber weight in micrograms per inch. For wool, fineness is the mean fiber width or mean fiber diameter expressed in microns (to the nearest 0.001-millimeter). 2. For yarn fineness, see YARN NUMBER. 3. For fineness of knit fabrics, see GAUGE.
FINES: Particles or dust of polymer formed during the process of cutting to produce chip.
FINE STRUCTURE: Orientation, crystallinity, and molecular morphology of polymers, including fiber-forming polymers.
FINGER MARK: A defect of woven fabrics that is seen as an irregular spot showing variation in picks per inch for a limited width. Causes are spreading of warp ends while the loom is in motion and pressure on the fabric between the reed and take-up drum.
FINISH: 1. A substance or mixture of substances added to textile materials to impart desired properties. 2. A process, physical or chemical, performed on textile materials to produce a desired effect. 3. A property, such as smoothness, drape, luster, water repellency, flame retardancy, or crease resistance that is produced by 1 and/or 2 above. 4. The state of a textile material as it leaves a process. (Also see FINISHING.)
FINISH COMPOSITION (YARD): Physical and chemical analysis of the lubricant applied to yarns to reduce friction and improve processibility.
FINISHED FABRIC: Fabric that is ready for the market, having passed through the necessary finishing processes.
FINISHING: All the processes through which fabric is passed after bleaching, dyeing, or printing in preparation for the market or use. Finishing includes such operations as heat-setting, napping, embossing, pressing, calendering, and the application of chemicals that change the character of the fabric. The term finishing is also sometimes used to refer collectively to all processing operations above, including bleaching, dyeing, printing, etc.
FINISHING BAR: A noticeable streak across the entire width of a fabric, usually caused by machine stoppage during processing.
FINISHING SPOT: A discolored area on a fabric caused by foreign material such as dirt, grease, or rust.
| FINISH TURNS: The actual degree of twist in the final yarn product. FIRE-BLOCKING LAYER: A fabric layer composed of fibers with flame-retardant properties used in aircraft seat cushions and other upholstery constructions to decrease the overall flammability of the total construction by preventing access of flame to the body of the construction. | 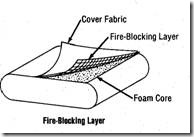 |
FIRST QUALITY: See YARN QUALITY. FISH EYE: See PINHOLE.
FISSURE: A very minute crack or opening in a material that frequently leads to the breaking or rupture of the material.
FIXATION: The process of setting a dye after dyeing of printing, usually by steaming or other heat treatment.
FLAKE: As used by Celanese, a term that refers to the granular form in which cellulose acetate and triacetate polymers exist prior to dissolving or feeding into the extrusion or molding unit.
FLAKE YARN: Yarn in which roving or short, soft staple fibers are inserted at intervals between long filament binder yarns.
FLAKY WEB: A web at the card that shows thick and thin places, approximately 1 to 6 square inches in size. This indicates that, instead of a free flow of fibers through the card, either an uneven amount has been fed into the card, or groups of fibers have hesitated in the card and then dropped back into production.
FLAME RESISTANCE TESTS: See FLAMMABILITY TESTS.
FLAME RESISTANT: A term used to describe a material that burns slowly or is self- extinguishing after removal of an external source of ignition. A fabric or yarn can be flame resistance because of the innate properties of the fiber, the twist level of the yarn, the fabric construction, or the presence of flame retardants, or because of a combination of these factors. (Also see FLAME-RETARDANT and INHERENT FLAME RESISTANCE.)
FLAME RETARDANT: A chemical compound that can be incorporated into a textile fiber during manufacture or applied to a fiber, fabric, or other textile item during processing or use to reduce its flammability. (Also see FLAME RESISTANT.)
FLAMMABILITY TESTS: Many procedures have been developed for assessing the flame resistance of textiles. The most common currently in use are detailed below:
Diagonal (45°) Flame Test: In this test for flame resistance, a
specimen is mounted at a 45° angle and exposed to an open flame
for a specific time. This test measures the ease of ignition and rate of burning of the samples.
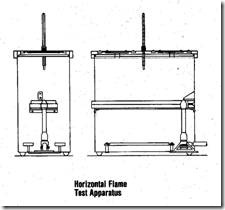
Horizontal Flame Test: A test for flame resistance in which a specimen is mounted in a horizontal holder and exposed to an open flame for a specific time to measure burning rate and char-hole diameter.


Methenamine Pill Test: A test for the flame resistance of carpets or rugs in which a methenamine tablet is ignited on a test sample under controlled conditions and the size of the burn hole is measured.
Mushroom Apparel Flammability Test: This test method involves igniting a cylinder of fabric around a core containing heat sensors and measuring the rate of heat transfer from the burning material to the sensor.
Radiant Panel Test: A test for the flammability of carpets or rugs in which the specimen is mounted on the floor of the test chamber and exposed to intense radiant heat from above. The rate of flame spread is assessed.

Smoke Chamber Test: This method assesses the smoke generating characteristics of a sample due to pyrolysis and combustion by measuring the attenuation of a light beam by smoke accumulating in a closed chamber under controlled conditions. Results are expressed in terms of specific optical density.
Tablet Test: See FLAMMABILITY TESTS, Methenamine Pill Test.
Thermo-Man: This instrumented mannequin system, interfaced with a computer, allows full scale testing of garments for protection capability or degree of flammability. The system was developed by Accurex Corporation for the U.S. Air Force.
Tunnel Test: Test for the flammability of floor coverings in which a sample is placed on the ceiling of a tunnel of specific dimensions and ignited under controlled conditions to determine the extent to which it will burn. (Also called Steiner Tunnel Test.)

Vertical Flame Test: A test for flame resistance in which a specimen is mounted in a vertical holder and exposed to an open flame for a specific time. The open flame is then extinguished and continued flaming time and char length of the sample are measured.
FLANGE CRIMPING: Simultaneous crimping of two ends of yarn by using heated snubber pins, then combining both ends on a draw roll after they contact a rubber flange on the draw roll.
FLANNEL: Mediumweight plain- or twill-weave, slightly napped fabric, usually of wool or cotton, but may be made of other fibers.
FLAPPER: The movable side of a fiber-crimping chamber that periodically opens or flaps to permit crimped fiber to be expelled from the chamber.
FLASH AGEING: A process for rapid reduction and fixation of vat dyes obtained when the printed fabric is padded with caustic soda and sodium hydrosulfite and immediately steamed in air-free steam.
FLASH SPINNING: See SPINNING, 5.
FLAT: In carding, one of the parts forming an endless chain that partially surrounds the upper portion of the cylinder and gives the name to a revolving flat card. Flats are made of cast iron, T- shaped in section, about 1 inch wide, and as long as the width of the cylinder. One side of the flat is nearly covered with fine card clothing, and the flats are set close to the teeth of the cylinder so as to work point against point. A chain of flats contains approximately 110 flats and operates at a surface speed of about 3 inches per minute.
FLAT ABRASION TESTER: See STOLL-QUARTERMASTER UNIVERSAL WEAR TESTER.
FLAT CARD: The type of card used for cotton fibers and for cotton-system processing. It is named for the flat wire brushes called flats that are assembled on an endless chain that partially surrounds the main cylinder. The staple is worked between the flats and cylinder, transferred to a doffer roll, and peeled off as a web that is condensed into a sliver. (Also see FLAT.)

FLAT DUCK: See DUCK.
FLAT-KNIT FABRIC: 1. A fabric made on a flat-knitting machine, as distinguished from tubular fabrics made on a circular-knitting machine. While tricot and milanese warp-knit fabrics (non-run) are knit in flat form, the trade uses the term flat-knit fabric to refer to weft-knits fabrics made on a flat machine, rather than warp-knit fabrics. 2. A term used in the underwear trade for plain stitch fabrics made on a circular-knitting machine. These fabrics have a flat surface and are often called flat-knit fabrics to differentiate them from ribbed-knit or Swiss rib fabrics. In this case, the term refers to the texture, not the type of machine on which the fabric was knit.
FLAT KNITTING: See KNITTING.
FLAT-KNITTING MACHINE: A weft-knitting machine with needles arranged in a straight line in a flat plate called the bed. The yarn travels alternately back and forth, and the fabric may be shaped or varied in width, as desired, during the knitting process. Lengthwise edges are selvages. Flat-knitting machines may be divided into two types: latch-needle machines for sweaters, scarves, and similar articles and fine spring-needle machines for full-fashioned hosiery.
FLATSPOTTING: A characteristic of certain tire cords. It occurs with all materials but is more noticeable with nylon cord and is associated with nylon cord by users. Nylon exerts a shrinkage force as it becomes heated in tire operation. When the tire is stopped under load, the cord in the road-contact portion of the tire is under less tension than that in other portions of the tire, and it shrinks to conform to the flat surface of the road. When cooled in this position, the cord maintains the flat spot until it again reaches its glass transition temperature in use.
FLAT-TOP CARD: See FLAT CARD.
FLAX: The plant from which the cellulosic fiber linen is obtained.
FLEECE FABRIC: A fabric with a thick, heavy surface resembling sheep’s wool. It may be a pile or napped fabric of either woven or knit construction.
FLEX ABRASION TESTER: See STOLL-QUARTERMASTER UNIVERSAL WEAR TESTER.
FLEXIBILITY: 1. The ability to be flexed or bowed repeatedly without rupturing. 2. A term relating to the hand of fabric, referring to ease of bending and ranging from pliable (high) to stiff (low).
FLEXURAL FATIGUE: A physical property expressed by the number of times a material can be bent on itself through a prescribed angle before it ruptures or loses its ability to recover.
FLEXURAL RIGIDITY: This measure of a material’s resistance to bending is calculated by multiplying the material’s weight per unit area by the cube of its bending length.
FLOAT: 1. The portion of a warp or filling yarn that extends over two or more adjacent filling picks or warp ends in weaving for the purpose of forming certain designs. 2. In a knit fabric, a portion of yarn that extends for some length without being knitted in. 3. A fabric defect consisting of an end lying or floating on the cloth surface instead of being woven in properly. Floats are usually caused by slubs, knot-tails, knots, or fly waste, or sometimes by ends being drawn in heddle eyes incorrectly or being twisted around heddle wires.
FLOATING ENDS: See FLOAT, 3.
FLOAT STITCH: See MISS-STITCH.
FLOCCULATING: Coagulating or coalescing a material into a small, loosely aggregated mass.
FLOCK: The material obtained by reducing textile fibers to fragments by cutting or grinding. There are two main types: precision cut flock, where all fiber lengths are approximately equal,
and random cut flock, where the fibers are ground or chopped to produce a broad range of lengths.
FLOCKING: A method of cloth ornamentation in which adhesive is printed or coated on a fabric, and finely chopped fibers are applied all over by means of dusting, air-blasting, or electrostatic attraction. In flock printing, the fibers adhere only to the printed areas and are removed from the unprinted areas by mechanical action.

FLUFFING: A term describing the appearance of a carpet after loose fiber fragments left during manufacture have worked their way to the surface. Fluffing is not a defect; it is simply a characteristic of new carpets that disappears with vacuuming.
FLUORESCENCE: Emission of electromagnetic radiation, usually as visible light, that is caused by the flow of energy into the emitting body. The emission ceases abruptly when the excitation ceases.
FLY: The short, waste fibers that are released into the air in textile processing operations such as picking, carding, spinning, and weaving.

FLYER: 1. A device used to insert twist into slubbing, roving, or yarn, and to serve as a guide for winding it onto a bobbin. The flyer is shaped like an inverted U that fits on the top of the spindle and revolves with it. One arm of the U is solid and the other is hollow. The yarn enters through the top of the hollow arm, travels downward, and emerges at the bottom where it is wound around a presser finger onto the take-up package. 2. See LOOM FLY.
FLYER SPINNING: A method of spinning by means of a driven flyer. It is used primarily for spinning worsted and coarser yarns. (Also see FLYER, 1.)
FLYER SPINNING FRAME: See SPINNING FRAME.
FLYER WASTE: During the roving operation, flyer waste refers to fibers that free themselves by centrifugal force from the regular bulk of roving and accumulate on the flyers and adjacent machinery.
FLY FRAME: See ROVING FRAME.
FOAM: Dispersion of gas in a liquid or solid. The gas bubbles may be any size. The term covers a wide range of useful products such as insulating foam, cushions, etc. It also describes the undesirable froth in polymer melts, dyebaths, etc.
FOLDED SELVAGE: A curled selvage. FOLDED YARN: See PLIED YARN.
FOREIGN WASTE: Thread waste or lint that is twisted in the yarn or woven in the fabric. If such foreign matter is of a different fiber, it may dye differently and thus show plainly.
FORMALDEYDE: A one-carbon aldehyde, (CH2O), it is a colorless, pungent gas at room temperature. This compound is used primarily for disinfectant and preservative and in synthesizing other compounds and resins.
FORMED FABRIC: See NONWOVEN FABRIC.
FOULARD: A lightweight, lustrous 2/2 twill that is usually printed with small figures on a solid background, foulard is frequently used in men’s ties. Foulards are made of silk, filament polyester, acetate, etc.
FRAME: 1. A general term for many machines used in yarn manufacturing such as the drawing frame, roving frame, and spinning frame. 2. See TENTER FRAME.
FRAMEWORK KNITTING: See KNITTING, Weft Knitting.
FRAYING: The slipping or raveling of yarns from unfinished edges of cloth.
FREE-WHEELING: In reference to rolls, spinning without the application of either driving or braking force.
FRENCHBACK: A fabric with a corded twill backing of different weave than the face. The backing, which is frequently of inferior yarn, gives added weight, warmth, and stability to the cloth.
FREQUENCY: In uniform circular motion or in any periodic motion, the number of revolutions or cycles completed in unit time.
FRICTION FALSE-TWIST TEXTURING: See TEXTURING, False-Twist Method.

FRICTION SPINNING: A spinning system in which the yarn receives its twist by being rolled along the longitudinal axis in the nip between two revolving surfaces. The surfaces may rotate at the same or different speeds in the same or opposite directions depending on the particular machine design. Potential advantages include high production capacity, low stress on the fiber in processing, and the capacity to produce very fine counts.
FRIEZÉ: 1. A term applied when the pile of a velvet, plush, velour, or other pile fabric is uncut. A friezé fabric is sometimes patterned by shearing the loops at different lengths. Friezé fabrics are widely used for upholstery. 2. A cut-pile carpet made of highly twisted yarns normally plied and heat-set. A kinked or curled yarn effect is achieved. Excellent durability results from the hard-twist pile yarns.
FROSTING: See COLOR ABRASION.
FROST MARKS: A defect of woven fabric consisting of surface highlights that give a frosted appearance. Frost marks are caused by improper sizing or insufficient warp tension as a result of uneven bending of some warp ends over the picks.
FULL-FASHIONED: A term applied to fabrics produced on a flat-knitting machine, such as hosiery, sweater, and underwear, that have been shaped by adding or reducing stitches.
FULLING: A finishing process used in the manufacture of woolen and worsted fabrics. The cloth is subjected to moisture, heat friction, chemicals, and pressure which cause it to mat and shrink appreciably in both the warp and filling directions, resulting in a denser, more compact fabric.
FUME FADING: See GAS FADING.
FUSED ACETATE: 1. A hard particle of acetate material of almost any shape or size other than recognizable fiber. Sometimes fused acetate particles resemble rock-like, hardened drops of acetate dope; in other cases fused acetate consists of particles covered with fiber clusters and completely hardened in the center. 2. Acetate yarns in which the individual filaments are coalesced.
FUSED FILAMENTS: A group of filaments bonded together in a tow by drips or frictional effects and thereby resistant to filament separation and crimp deregistering.
FUSED RIBBON: Acetate fabrics in wide widths may be cut into narrow ones by the application of heat. A hot knife blade caused the edges to sear and bead, thereby doing away with selvages on the edges of the goods.
FUSING: 1. Melting. 2. Uniting, as by melting together.
FUZZ BALL: See BALLING UP.
FUZZINESS: 1. A term describing a woven fabric defect characterized by a hairy appearance due to broken fibers or filaments. Principle causes are underslashed warp; rough drop wires, heddles, or reed; fabric slippage on take-up drum; rough shuttles; cut glass, dents, or reeds in warper; and damage in slashing. 2. A term describing a fabric intentionally made with a hairy surface; such fabrics are usually produced from spun yarns.