Characteristics Of Spun Yarns
· Composed of short staple fibers· Made from cotton, flax or wool staple fibers
· Made from natural or man-made filaments which are cut into filament staple
· Individual fiber lengths vary
· Fuzzy appearance and feel
· Uneven number of fibers throughout
· Range from soft, loose construction to hard fine twist yarn
· Thick and thin areas
· Highly twisted
· Fall apart when untwisted
· Dull or flat in appearance
· Rough to the touch
· Natural textural appearance and feel
· Bulkier to the feel
· Provide good covering power
· Snagging depends on fabric structure
· Pilling depends on fiber content
Material Processing On The Short Staple System



Functions Of The Opening Process
· Open· Clean (natural fibers)
· Blend
Creating The Proper Bale Laydown
Coordination with Fiber Properties
· More variables in raw stock means more bales needed to laydown
· Must decide which variables have the greatest influence in yarn manufacturing.
Coordination with Fiber Inventory
· Laydown should be a "mini" representation of the warehouse inventory.
· . Laydown should be as consistent as possible from day-to-day, week-to-week, and month-to-month.
Blending
Blending is a process involving
· Measurement of the important fiber properties of length, fineness, strength, grade, color, etc.
· Proportioning and combining these properties under controlled conditions and in such a way that the physical properties of resultant blend can be predicted, are known, and are reproducible.
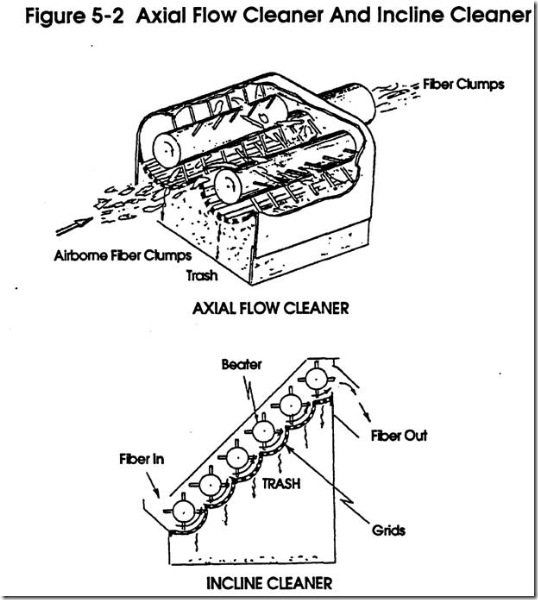
Fiber Opening And Cleaning
· Why fiber must be opened
· Principles of opening
· Why cotton must be cleaned
· Principles of cleaning


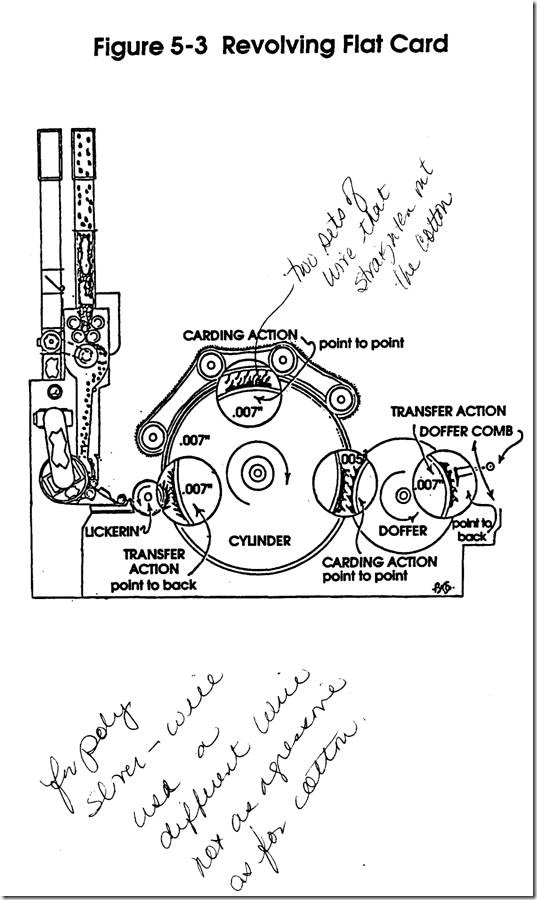
Carding
Materials Processed
Input -Output
v
Objectives of the Process
1. Open
2. Clean
3. Straighten
4. Blend
5. Draft
6. Package
Card Feeding Systems

Drawing
Material Processed
Input -Output -
Objectives of the Process
1. Improve sliver uniformity A. Doubling
2. Straighten fibers A. Drafting
3. Package sliver
Some General Definitions

The Combing Process
Purpose of Combing
Comber Preparation
Combining Organization
Basic Operations of Combing
1. Feeding the stock from a prepared lap.
2. Combing out short fibers, foreign particles and neps; parallelizing fibers.
3. Detaching the combed fibers from the lap.
4. Piecing up the fleecy tuft of combed fibers with the fibers in the returned web.
5. Condensing the combed web into sliver and doubling the sliver on the table.
6. Drafting the doubled slivers through the draw box.
7. Calendering and packaging the combed sliver into a container for further handling and processing.

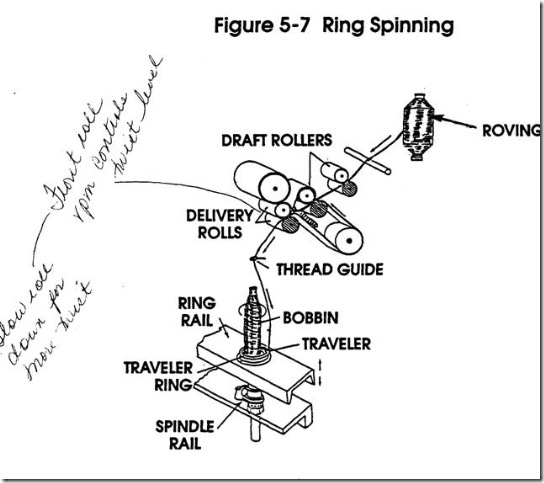
Roving
Materials Processed Input -
Output -
Objectives of the Process
1. Draft
2. Twist 3. Package
Operations on Roving Frame,
1. Drafting
2. Twisting
3. Laying
4. Winding 5. Building


Rotor - Type Open End Spinning
Material Processed
Input -Output -
Objectives of the Process
1. Open
2. Draft 3.. Align
4. Twist
5. Wind
Figure 5-8 The Principal Of Open-End Spinning


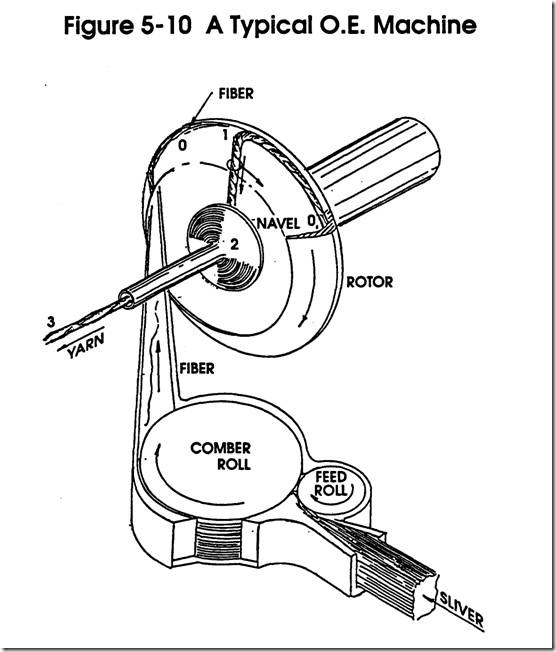
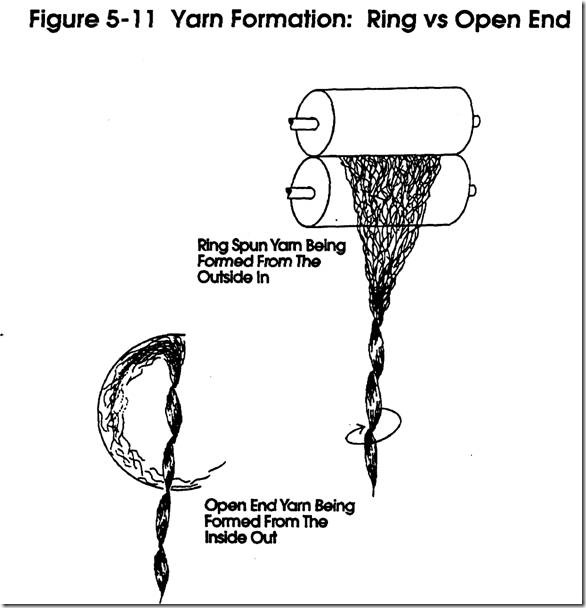


Figure 5-13 Formation And Structures Of Air Jet
Spun Yarns
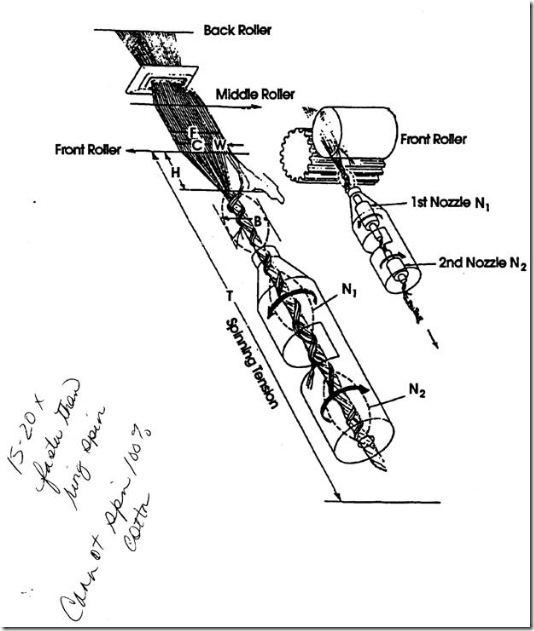
Figure 5-14 Wrap Spinning Process

Methods Of Expressing Twist

Spindle rotating clockwise produces Z Twist.
Spindle rotating counter-clockwise produces S Twist. Spun Yarns
Singles use T.M.
Ply use T.M. and T.P.I.
Filament Yarns Use T.P.I.

For Cotton Yarns
Knitting T.M. 2.2 to 3.5
Filling T.M. 3.5 to 4.2
Warp T.M. 4.2 to 5.0
Voile & Crepe T.M. 5.0 to 7.0
Effects Of Twist On Yarn And Fabric Properties
Degree of Yarn Twist Affects the Yarns
· Diameter or fineness
· Contraction
· Softness or hardness (hand)
· Bending behavior
· Absorbency
· Covering power
· Permeability
· Tensile strength
· Elastic performance/Extension and recovery
· Resistance to creases and abrasion
· Pilling behavior
· Luster
Degree of Yarn Twist Affects the Fabrics
· Hand
· Appearance
· Texture
· Drapability qualities
· Performance expectations
· . Durability
· Serviceability
Plied Yarn
Yarn Is Plied To
· Introduce different fiber yarns
· Combine spun and filament yarns
· Add to or increase the strength of single strand yarns
· Utilize multi-strands of fine yarns to produce a thick strand
· Produce a smoother yarn
· Produce a yarn with uniform diameter
· Introduce textured or novelty yarns
· Add color interest
Characteristics of Plied Yarns
· Thicker and heavier
· Coarse
· Differ in count
· Less flexible than single yarns
· Affect drapability quality of fabric
· May be constructed with no twist at all
· May be highly twisted
· May differ in tension and direction of twist
Figure 5-15 Novelty Yarns
